Today I will perform a comparison test to understand the difference between SSD and HDD disk drive effect on site performance. Most of the cheap shared hosting servers are built on mechanical hard drives (HDD) that cause complications like high CPU usage, slow loading, etc.
I am using Google Cloud’s Standard Persistent Disk (HDD) vs. SSD Persistent Disk (SSD) and comparing the same website setup for testing purposes. I already have an e-commerce demo setup that is not at all optimized; it’s bloated with plugins and third-party scripts to make it realistic.
The HDD mimics the shared hosting servers like BlueHost, Hostgator, etc., while the SSD mimics the cloud VPS servers like DigitalOcean, WPEngine, etc.
I’ll run three tests on each of these testing tools and will be considering the 3rd test as the final result. It will take the CPU and Memory performance from the SSH login using the htop command after performing a load test with 20 simultaneous unique visitors.
I’ll also add the load test results, which can help understand load performance and any misfires. I hope you’re now excited as I am; hence let’s get started —
Site Performance on HDD Hosting
I did the demo e-commerce site test on all the significant speed and performance testing tools. As I mentioned, the server is not optimized for a performance boost. It doesn’t even have an essential caching plugin.
Please click on the image to view in actual size and keyboard navigation.
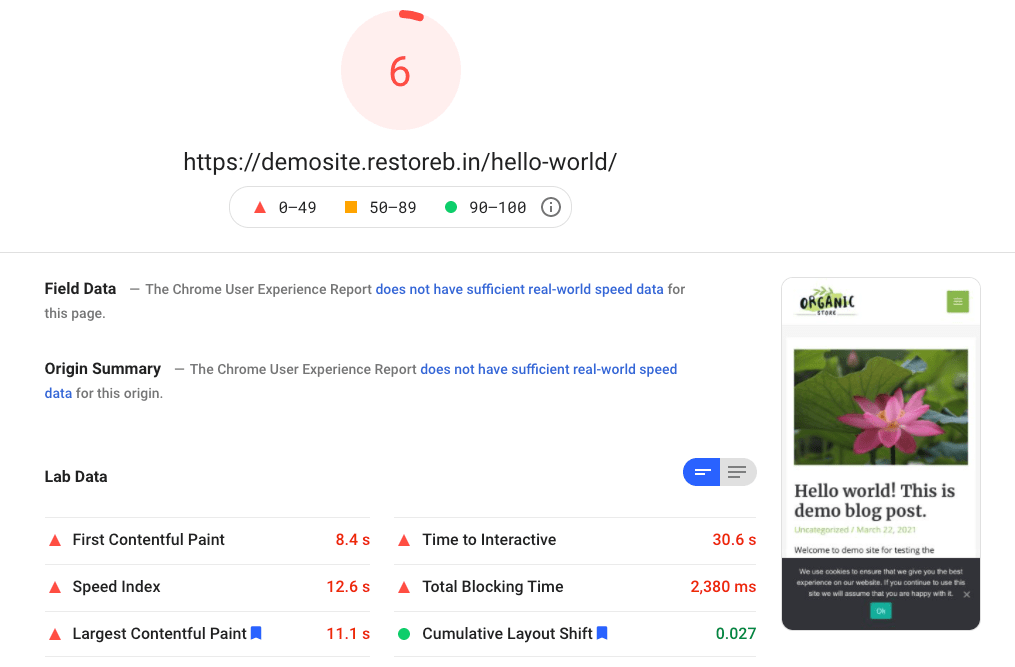
Here are the test results of the website when running on the HDD disk:
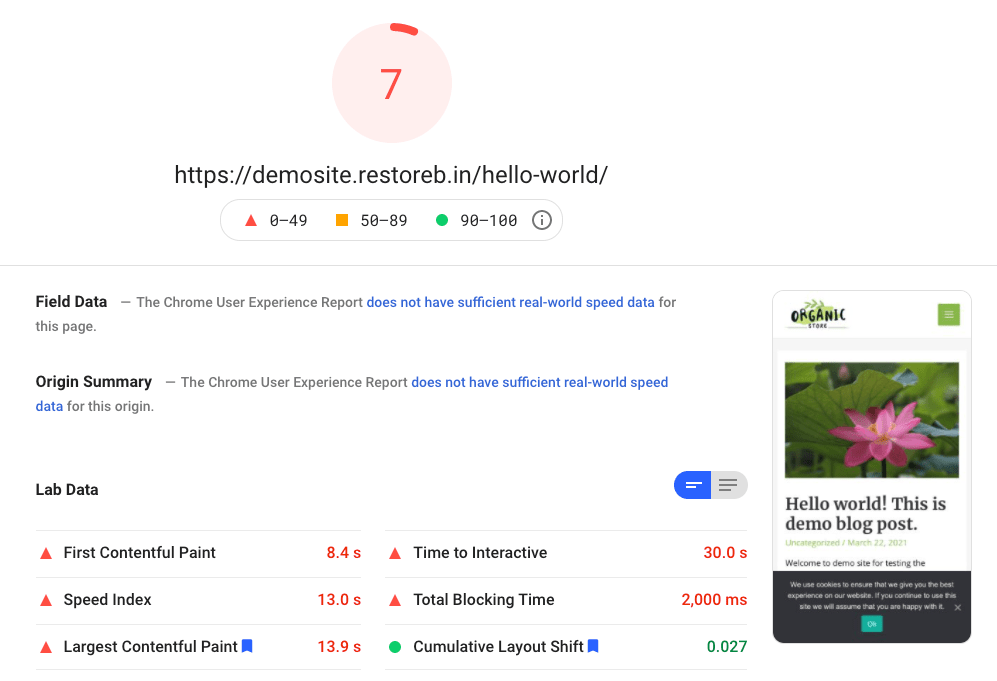
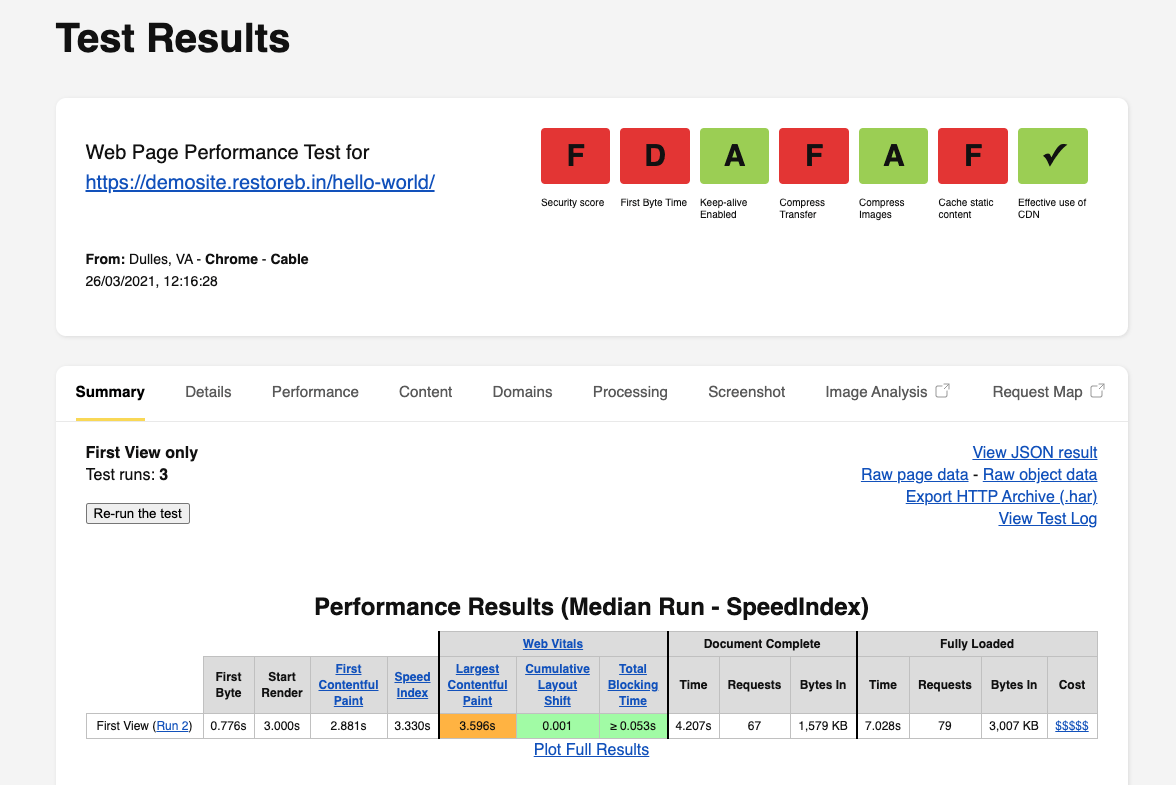
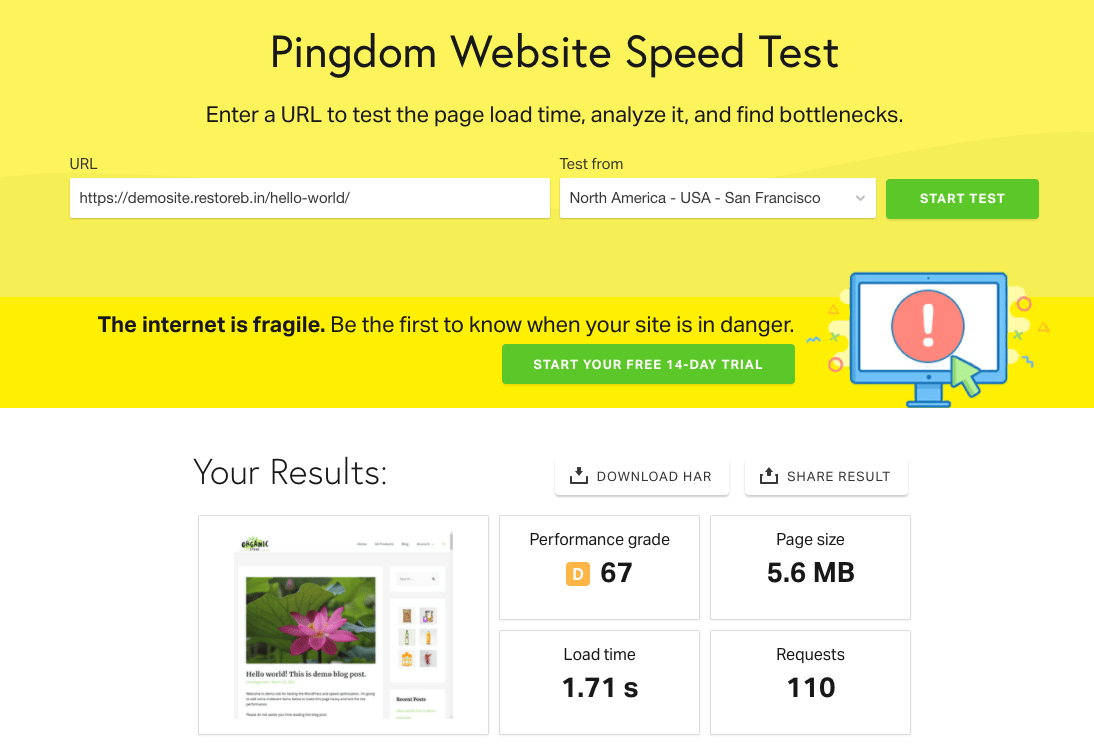
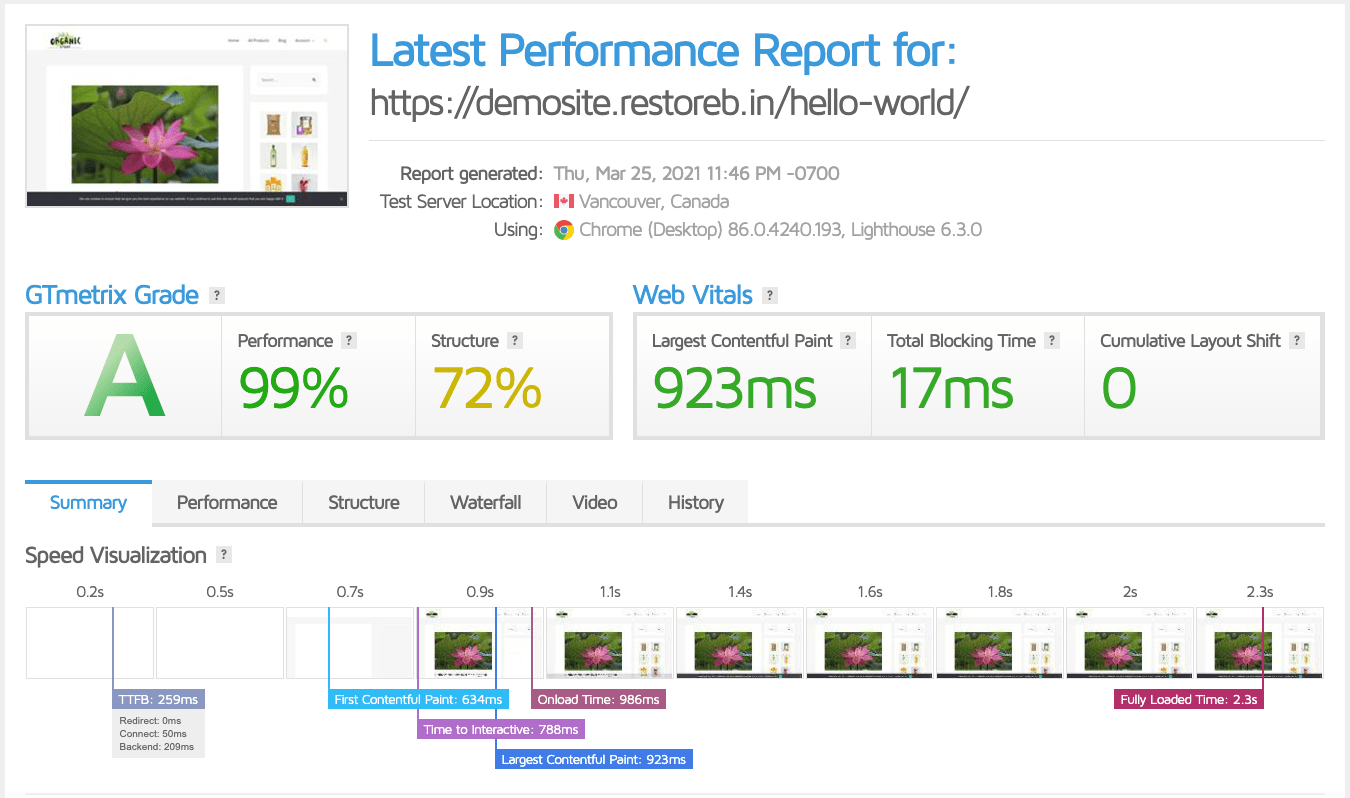
Looking at the test results, it seems the website is slow and has inferior performance on the HDD storage disk. Anyways, let’s move ahead with the SSD server.
Site Performance on SSD Server
I cloned the same site and data into an SSD server with a similar hardware configuration (RAM, Memory Size, etc.). Pointing the DNS Setting IP address to the new SSD server can resolve the same site URL. There are no changes except the HDD being replaced with SSD.
Here are the test results of the same website when on an SSD disk:
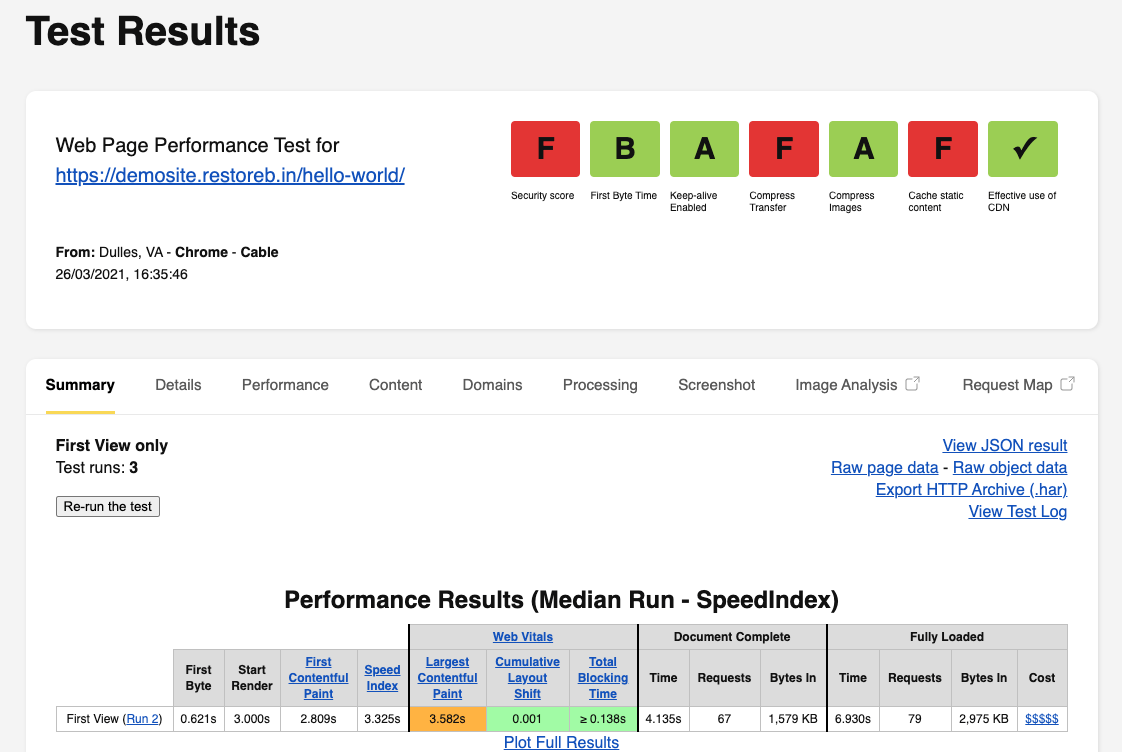
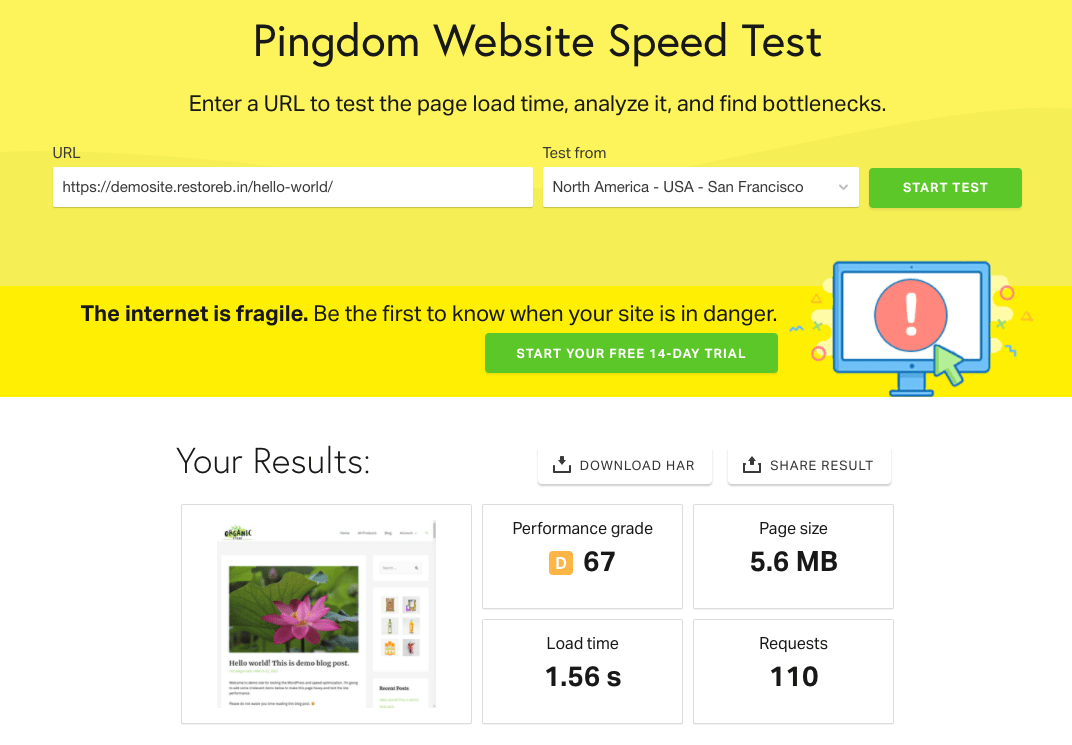
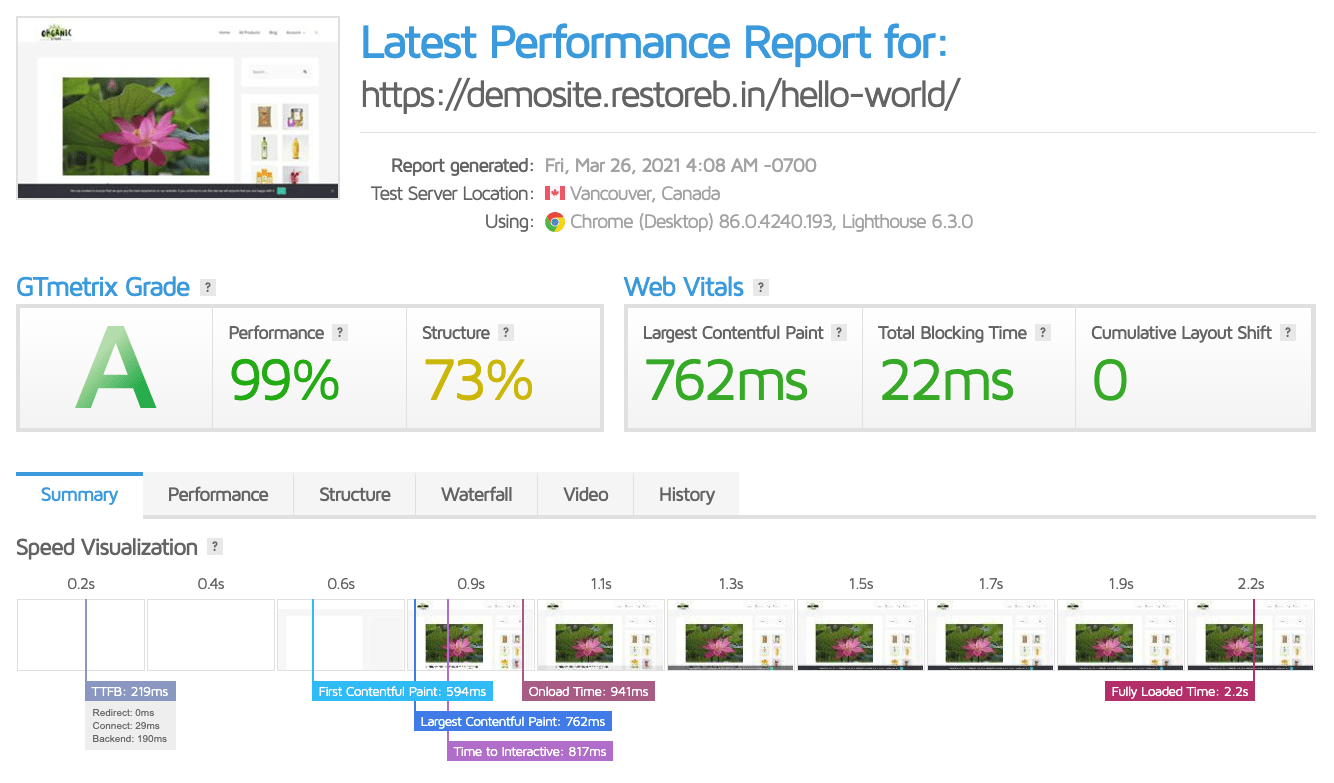
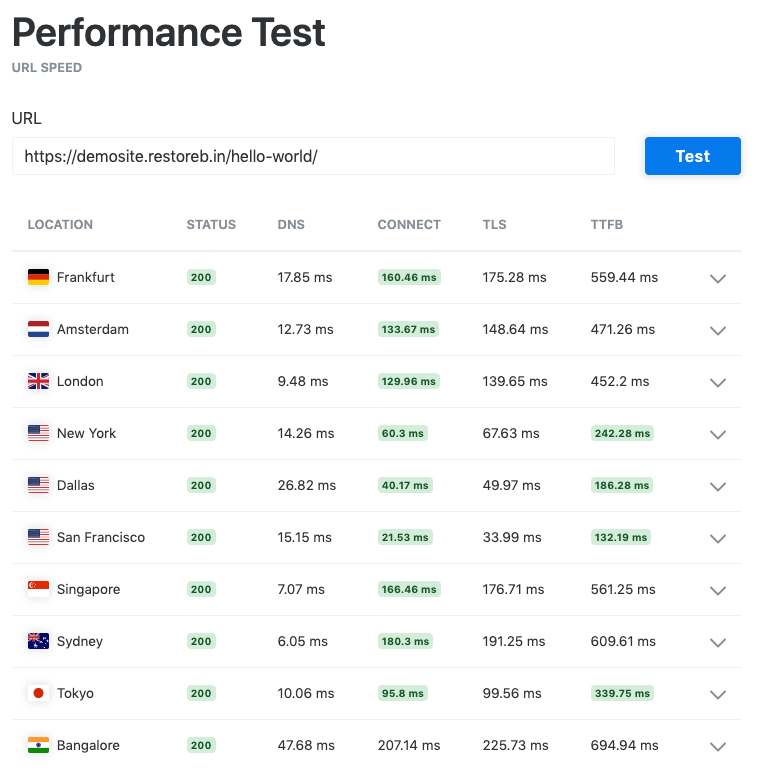
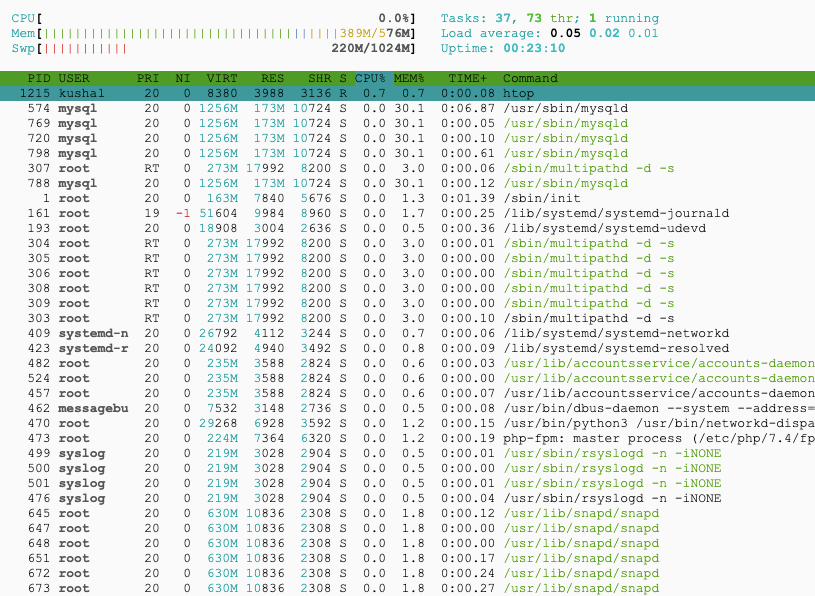
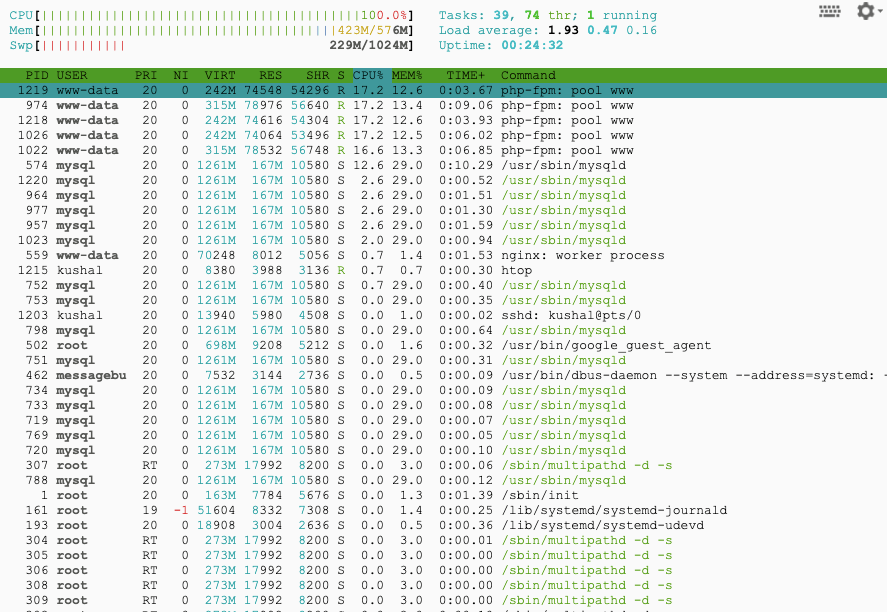
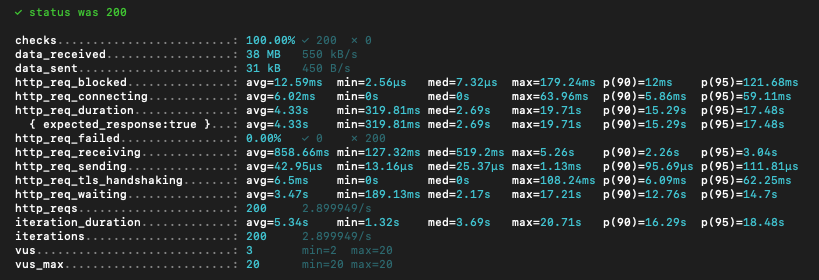
The overall site performance is still poor, even on the SSD server. However, we can see actual upgrades when comparing the performance difference between SSD vs. HDD servers.
Comparing HDD Vs. SSD Hosting
Now let’s compare Apple to Apple under each testing tool.
Google PageSpeed Insight:


I only considered Mobile reports since desktop consistently outperforms mobile, and Google considers mobile-first as SEO ranking.
- If you look at the score, the HDD has one point extra compared to the SSD due to better Total Blocking Time and Time to Interactive.
- Another essential metric, Speed Index, is better for SSD servers.
- All other metrics are nearly the same and poor.
WebPageTest:


- The ratings for important metrics are almost the same except for the First Byte Time, which is far better for the SSD server.
- If you look at the performance result, the SSD has slightly outperformed over HDD in every category.
Pingdom Tool:


- The Load time of the SSD server is 150ms better than HDD.
- All other metrics and performance grades are the same.
GTMetrix:


- The GTmetrix Grade for both hardware setups is almost the same.
- However, the Total Blocking Time under Web Vitals for SSD is slightly poor.
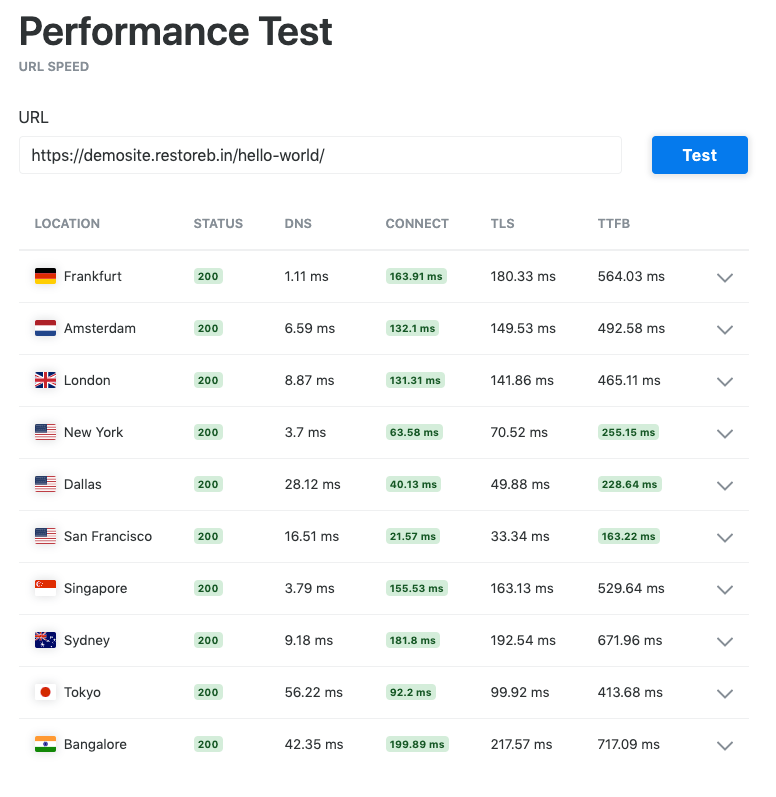
KeyCDN Performance Tool:


- If you compare the TTFB (Time for First Byte), every location under the SSD server has outperformed the HDD host (except Singapore).
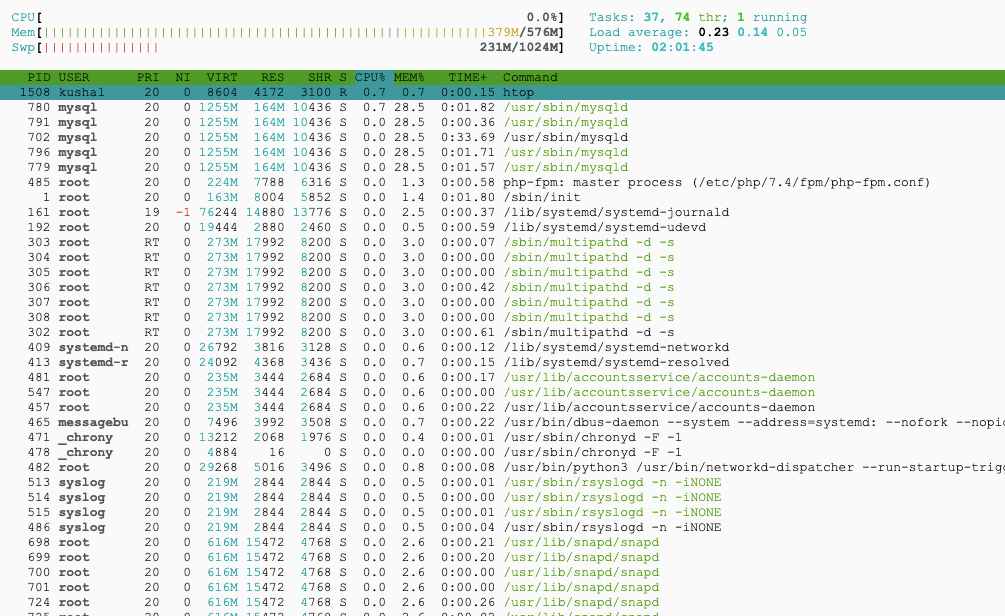
CPU and Memory Utilization:
These are the result of server utilization before performing the load test on the server.


- There is no significant difference in CPU, Memory, and Swap utilization between SSD and HDD without any users.
- But, the HDD is on the higher side compared to SSD hosting.
- The load average is relatively higher in the HDD.
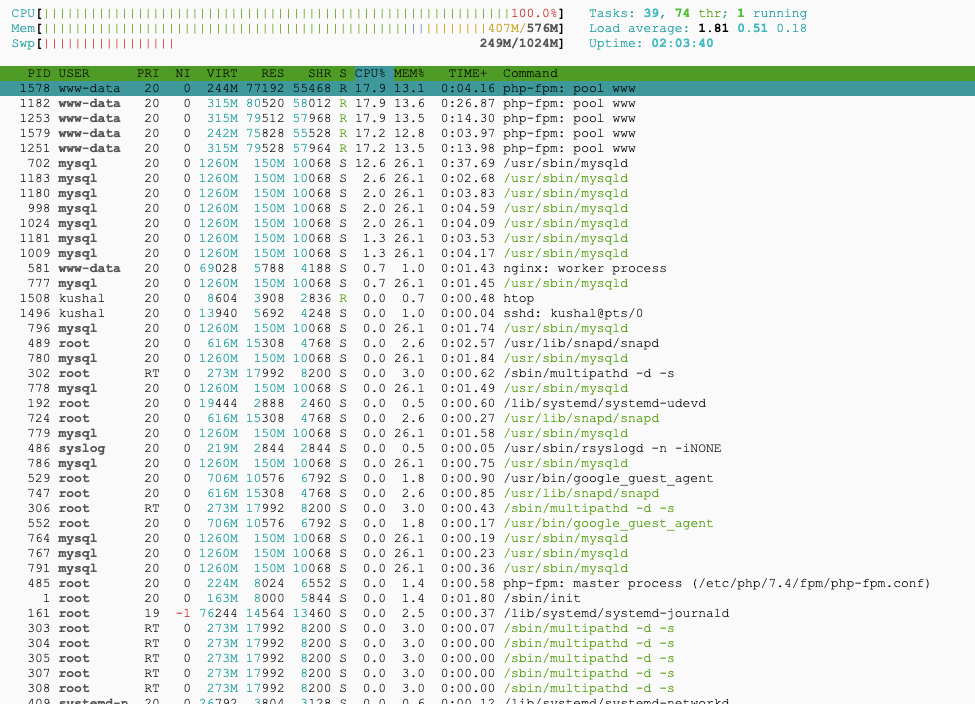
These are the result of server utilization while performing the load test.


- The CPU is 100% utilized for both SSD and HDD hosting.
- Memory and Swap usage are slightly lower for SSD when compared to HDD.
- The load average is nearly the same.
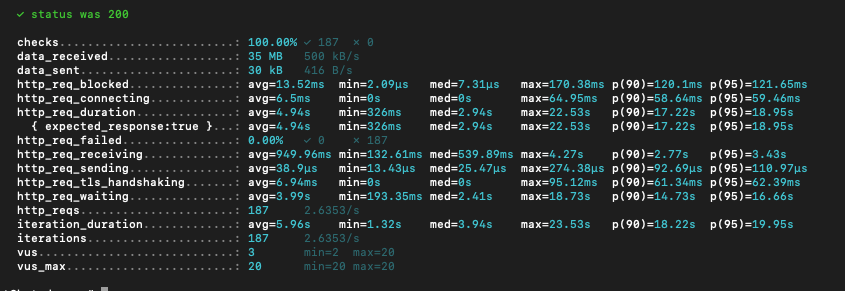
These are load test results performed using the K6 open source program.


- The SSD has handled more requests than HDD; hence we have more Memory and Swap utilization on the server.
- The SSD has outperformed the HDD in every aspect.
- There are no failed requests even after 100% CPU utilization. That’s because of the virtually shared CPU, aka vCPU.
Net-net, I can say that SSD is better when compared with HDD-hosted sites. We get a full bare metal capability with SSD that can be further enhanced after optimization.
Conclusion: SSD vs. HDD server hosting
There is no significant difference when comparing sites hosted on unoptimized SSD servers and HDD servers. However, when we optimized the web servers and the website, we noticed the difference in my bucket list for a future article.
With all the test results above, we can decide which is better hosting hardware. If we optimize the server and use the SSD capability to the full extent like Nginx Cache, we can further improve the performance and site speed.
The HDD will limit us from making server-side improvements and often max out due to low disk writing speed and high CPU utilization.
If you’re considering switching to SSD-based hosting, I strongly recommend using DigitalOcean Cloud VPS. I have been a proud and happy customer for seven years. They recently added NVMe SSD with Intel and AMD processors as premium servers which is even better than regular SSD.


Hi,
I like your website design. I have a doubt. How do you make ad sticky in the sidebar? Please explain
I use Q2W3 Fixed Widget plugin.
Thank you for the reply! I use the same for my website ******* [website redacted]. But when a user scrolls down to the footer, your ad is not fixed. But in my case, when a user scrolls down, the footer is cut. Please help me with how to do it. If possible, write a blog on this topic.
There is an option called Stop Element in plugin settings, add
#footerwithin it.